 Introduction to Direction of India's Foreign Trade ↓
Introduction to Direction of India's Foreign Trade ↓
By direction of trade we mean the countries with which India keeps international trade relations. It also helps us to understand the diplomatic relations maintained by India with other countries in direction of trade.
For the purpose of direction of trade, the countries to which India exports are broadly divided into following five groups.
The group of countries to which India Exports are :-
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation & Development (OECD) comprising of USA, Canada, European Union (EU), Australia and Japan.
- Organisation of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) which includes Kuwait, Iran, Iraq, Saudi Arabia and others.
- Eastern Europe which includes Romania, Russia and others.
- Developing Nations which includes China, Hong Kong, South Korea, Singapore and Malaysia.
 A. Direction of India's Exports ↓
A. Direction of India's Exports ↓
The above table reveals following changes in India's Exports :-
1. OECD
The OECD group accounted for a major portion of India's exports. The share of this group was 56.4% in 1990-91 & 44.3% in 2005-06. About 45% of these exports have been to European Union (EU) countries.
2. OPEC
The share of OPEC which was 5.6% in 1990-91. In 2005-06 it has increased to 14.8% i.e. share of OPEC has been showing an upward trend since 1990-91.
3. Eastern Europe
There was a rapid decrease in the share of Eastern Europe particularly U.S.S.R. Due to political problems & disintegration of the U.S.S.R, the share of Eastern Europe decreased from 17.9% in 1990-91 to 1.9% in 2005-06.
4. Developing Countries
The share of developing nations increased from 17.1% in 1990-91 to 38.7% in 2005-06. Asian countries now account for 1/4th of India's export earnings. Among the Asian countries the major export destinations have been Hong Kong, Singapore & Thailand.
5. Other Countries
The share of other countries has declined from 3.00% in 1990-91 to 0.3% in 2005-06.
 Important Facts of India's Country Wise Exports ↓
Important Facts of India's Country Wise Exports ↓
- The share of U.K in India's exports declined from 26.9% in 1960-61 to 4.5% in 2004-05.
- The share of USA in India's exports was 16% in 1960-61 and it rose to 16.7% in 2004-05. India was dependent on U.K and U.S.A for 43% of its export earnings in 1960-61. US to be the single largest trading partner for India but with a declining trend.
- The share of U.S.S.R. (Russia) rose from 4.5% in 1960-61 to 18.3% in 1980-81 but declined to 0.8% in 2004-05 due to the disintegration of U.S.S.R. Between 1986-90, the first position was occupied by U.S.A, second position by U.S.S.R and the third position by Japan. The position changed markedly after the disintegration of U.S.S.R.
- In the recent years, export to East Asian Countries has increased, mainly Hong Kong, Singapore and Thailand.
- There has been a healthy growth of bilateral trade between India and China. In the first seven months of 2002-03, Indo-China bilateral trade expanded by 43.4%. China is the second largest trading partner for India next to USA.
 B. Direction of India's Imports ↓
B. Direction of India's Imports ↓
Since the last decade, there has been a distinct shift in the direction of trade. The share of OECD countries both in exports & imports is on the decline. Eastern Europe is no more a major partner in our trade. Its share has reached the lowest among the group. The Asian developing countries are becoming important trade partners.
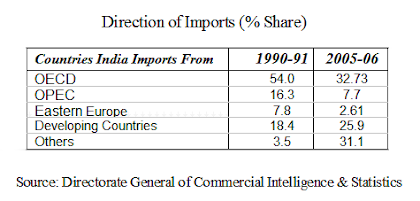
The above table reveals following changes in India's Imports :-
1. OECD - Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
The share of OECD in India's import expenditure declined from 54% in 1990-91 to 32.73% in 2005-06. Thus the importance of OECD declined over the period 1990-91 to 2005-06.
2. OPEC - Organisation of Petroleum Exportinq Countries
OPEC mainly include Iran, Iraq, Kuwait and Saudi Arabia. The share of OPEC countries decreased from 16.3% in 1990-91 to 7.7% in 2005-06 mainly because of crude oil. There has been a change in the source of oil imports from OPEC to other countries.
3. Eastern Europe
This includes mainly the former USSR. India's share of imports from Eastern Europe has also declined from 7.8% in 1990-91 to 2.6% in 2005-06. This is mainly due to decline in imports from Russia.
4. Developing Nations
This includes the developing countries of Africa, Asia, Latin America and Caribbean. The share of developing nations in India's import expenditure increased from 18.4% in 1990-91 to 25.9% in 2005-06.
5. Other Countries
The share of other countries increased from 3.5% in 1990-91 to 31.1% in 2005-06.
 Important Facts of India's Country Wise Imports ↓
Important Facts of India's Country Wise Imports ↓
- The share of U.S.A in India's imports was 29.2% and that of U.K was 19.4% in 1960-61. U.S.A. ranked first and U.K ranked the second. During the whole planning period, India has obtained maximum imports from U.S.A.
- With the emergence of new trading partners like Japan, Germany and Canada the dependence on U.K. declined. The share of U.K. in Indian imports declined from 19.4% in 1960-61 to 3.2% in 2004-05.
- Trade with Japan increased in absolute terms and India has now entered in to a number of collaborations with Japan. The percentage share of Japan has decreased from 5.4% in 1960-61 to 2.8% in 2004-05.
- Trade with USSR occupied the second place next to USA, during 1984. The share of USSR increased from 1.4% in 1960-61 to 10.4% in 1984-85. With the disintegration of USSR, the share of Russia fell to 1.2% in 2004-05. The directions has now changed markedly.
- The share of developing countries has constituted more than 1/4th of total imports in 2004-05 of these imports from Asian countries are most important.
 Conclusion on Direction of India's Foreign Trade ↓
Conclusion on Direction of India's Foreign Trade ↓
Significant changes have taken place in the direction of India's foreign trade since 1991, and more particularly during the last two-three years. What's most significant is the emergence of China, Singapore, Hong Kong, South Korea & Malaysia as important trading partners of India from the Asian region, Switzerland from OECD countries, and UAE & Indonesia (which left OPEC in 2008) from OPEC countries.
However, India should cultivate more trade relations with Africa, South America and Middle-East Asian Countries as these rich countries would offer huge markets for India's export.
The diversification of India's exports has fetched a cheaper source of imports and a bigger market for exports. India has established herself in the highly competitive world market in the recent years.


No comments:
Post a Comment